The data set used in this section is wjobs.dat. We would like to thank Amiram Vinokur and Bengt Muthén for making the data available.
The do-file is cace.do.
The program used is gllamm. Use the command ssc describe gllamm and follow instructions to download gllamm. For more information on gllamm see http://www.gllamm.org.
| depress | depression (response variable) |
| risk | baseline risk score |
| Tx | randomized to receive job training (1:yes, 0:no). This is r_j |
| basedep | baseline depression score |
| age | age in years |
| motivate | motivation to attend training |
| educ | school grade completed |
| assert | assertiveness |
| single | dummy for being single |
| econ | economic hardship |
| nonwhite | dummy for not being white |
| x10 | not used |
| c1 | complier in treatment group (1: complied, 0: did not comply). This is c_j |
| c2 | not used |
Read and prepare data
infile depress risk r depbase age motivate educ /* */ assert single econ nonwhite x10 c c0 using wjobs.dat, clear gen y1 = c if r==1 /* compliance missing in control group */ gen y2 = depress gen id=_n reshape long y, i(id) j(var) drop if y==. tab var, gen(d) /* create dummies d1 and d2 */
List some data
list id var d1 d2 y r c if id==1 | id==2 | id==175 | id==176, clean
id var d1 d2 y r c
1. 1 2 0 1 .45 0 1
2. 2 2 0 1 -.72 0 1
182. 175 1 1 0 0 1 0
183. 175 2 0 1 -1.37 1 0
184. 176 1 1 0 1 1 1
185. 176 2 0 1 .54 1 1
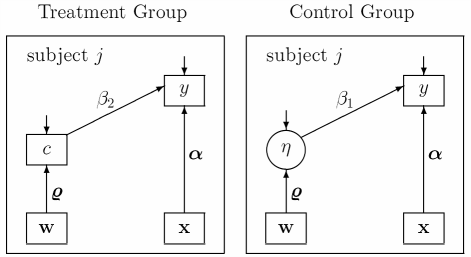
Path diagram of CACE model
Interactions and equations (for model without covariates)
gen nr_d2 = (1-r)*d2 gen c_r_d2 = c*r*d2 eq load: nr_d2 /* for beta_1(1-r_j)d_2i */
Constraints
cons def 1 [p2_1]_cons = [y]d1 /* constraint for varrho */ cons def 2 [z2_1_1]nr_d2 = 1 /* e_1 = 1 */ cons def 3 [z2_1_2]nr_d2 = 0 /* e_2 = 0 */
gllamm command for model without covariates in Table 14.6 (iteration log not shown)
gllamm y d1 d2 c_r_d2, i(id) eqs(load) l(logit ident) /*
*/ f(binom gauss) lv(var) fv(var) ip(fn) nip(2) /*
*/ constr(1/3) frload(1) nocons /* beta_1 is "freed" by frload(1) */
number of level 1 units = 837
number of level 2 units = 502
Condition Number = 5.8885922
gllamm model with constraints:
( 1) - [y]d1 + [p2_1]_cons = 0
( 2) [z2_1_1]nr_d2 = 1
( 3) [z2_1_2]nr_d2 = 0
log likelihood = -815.1493933028294
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d1 | .1855983 .1097431 1.69 0.091 -.0294942 .4006907
d2 | -.3909498 .0651724 -6.00 0.000 -.5186854 -.2632143
c_r_d2 | -.1224928 .0867746 -1.41 0.158 -.2925679 .0475822
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variance at level 1
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
.60067675 (.03791846)
Probabilities and locations of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (id)
loc1: 1, 0
var(1): .24785938
loadings for random effect 1
nr_d2: .01526969 (.17004298)
prob: 0.5463, 0.4537
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Estimate of Complier average causal effect:
lincom [y]c_r_d2 - [id1_1l]nr_d2
( 1) [y]c_r_d2 - [id1_1l]nr_d2 = 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
(1) | -.1377625 .141096 -0.98 0.329 -.4143056 .1387806
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Define more interactions to add covariates to the model
Make interactions with d1 (dummy for compliance response), for compliance model
gen age_d1 = age*d1 gen motivate_d1 = motivate*d1 gen educ_d1 = educ*d1 gen assert_d1 = assert*d1 gen single_d1 = single*d1 gen econ_d1 = econ*d1 gen nonwhite_d1 = nonwhite*d1
Add predictors of depression: make interactions with d2 (dummy for depression response)
gen depbase_d2 = depbase*d2 gen risk_d2 = risk*d2
New constraints: effects of covariates on compliance same in treatment and control groups
cons def 4 [p2_1]age = [y]age_d1 cons def 5 [p2_1]motivate = [y]motivate_d1 cons def 6 [p2_1]educ = [y]educ_d1 cons def 7 [p2_1]assert = [y]assert_d1 cons def 8 [p2_1]single = [y]single_d1 cons def 9 [p2_1]econ = [y]econ_d1 cons def 10 [p2_1]nonwhite = [y]nonwhite_d1
Estimate model with covariates for Table 14.6 using gllamm (iteration log not shown)
eq p: age educ motivate econ assert single nonwhite
eq load: nr_d2
gllamm y d1 age_d1 educ_d1 motivate_d1 econ_d1 assert_d1 single_d1 nonwhite_d1 /*
*/ d2 c_r_d2 depbase_d2 risk_d2, i(id) eqs(load) /*
*/ peqs(p) l(logit ident) f(binom gauss) lv(var) fv(var) ip(fn) nip(2) /*
*/ constr(1/10) frload(1) nocons
number of level 1 units = 837
number of level 2 units = 502
Condition Number = 508.29708
gllamm model with constraints:
( 1) - [y]d1 + [p2_1]_cons = 0
( 2) [z2_1_1]nr_d2 = 1
( 3) [z2_1_2]nr_d2 = 0
( 4) - [y]age_d1 + [p2_1]age = 0
( 5) - [y]motivate_d1 + [p2_1]motivate = 0
( 6) - [y]educ_d1 + [p2_1]educ = 0
( 7) - [y]assert_d1 + [p2_1]assert = 0
( 8) - [y]single_d1 + [p2_1]single = 0
( 9) - [y]econ_d1 + [p2_1]econ = 0
(10) - [y]nonwhite_d1 + [p2_1]nonwhite = 0
log likelihood = -729.4141540404285
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d1 | -8.740012 1.581554 -5.53 0.000 -11.8398 -5.640222
age_d1 | .0790446 .0140223 5.64 0.000 .0515615 .1065277
educ_d1 | .2997689 .0675165 4.44 0.000 .1674391 .4320987
motivate_d1 | .6668722 .1598218 4.17 0.000 .3536272 .9801172
econ_d1 | -.1586014 .1596605 -0.99 0.321 -.4715302 .1543274
assert_d1 | -.375871 .1464048 -2.57 0.010 -.6628191 -.0889229
single_d1 | .540194 .2754362 1.96 0.050 .0003489 1.080039
nonwhite_d1 | -.4985877 .3123484 -1.60 0.110 -1.110779 .1136038
d2 | 1.632537 .2791255 5.85 0.000 1.085461 2.179613
c_r_d2 | -.1299147 .0755598 -1.72 0.086 -.2780092 .0181798
risk_d2 | .9117567 .2624528 3.47 0.001 .3973587 1.426155
depbase_d2 | -1.463379 .1826867 -8.01 0.000 -1.821438 -1.10532
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variance at level 1
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
.50639704 (.0322776)
Probabilities and locations of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (id)
loc1: 1, 0
var(1): .00016
loadings for random effect 1
nr_d2: .1799526 (.1329182)
prob: 01.6e-04, 0.9998
log odds parameters
class 1
age: .0790446 (.01402225)
educ: .2997689 (.06751647)
motivate: .66687221 (.15982181)
econ: -.15860142 (.15966048)
assert: -.37587104 (.14640478)
single: .54019404 (.27543623)
nonwhite: -.49858773 (.31234837)
_cons: -8.7400116 (1.5815542)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Complier Average Causal Effect
lincom [y]c_r_d2 - [id1_1l]nr_d2
( 1) [y]c_r_d2 - [id1_1l]nr_d2 = 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
(1) | -.3098673 .1173219 -2.64 0.008 -.5398141 -.0799205
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vinokur, A. D., Price, R. H. and Schul, Y. (1995). Impact of JOBS intervention on unemployed workers varying in risk for depression. American Journal of Community Psychology 19, 543-562.
Little, R. J. A. and Yau, L. H. Y. (1998). Statistical techniques for analyzing data from prevention trials. Psychological Methods 3, 147-159.
Skrondal, A. and Rabe-Hesketh, S. (2004). Generalized
Latent Variable Modeling: Multilevel, Longitudinal and Structural
Equation Models. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press.
Outline
Datasets and do-files