The data set used in this section is mislevy.dat. Below we assume that this has been saved in the current directory.
The do-file is mislevy.do.
The programs we use are gllamm and gllapred. You can find the programs and download them by issuing the command findit gllamm and findit gllapred. For more information see http://www.gllamm.org.
Read and prepare the data
insheet using mislevy.dat, clear
list, clean
y1 y2 y3 y4 cwm cwf cbm cbf
1. 0 0 0 0 23 20 27 29
2. 0 0 0 1 5 8 5 8
3. 0 0 1 0 12 14 15 7
4. 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3
5. 0 1 0 0 16 20 16 14
6. 0 1 0 1 3 5 5 5
7. 0 1 1 0 6 11 4 6
8. 0 1 1 1 1 7 3 0
9. 1 0 0 0 22 23 15 14
10. 1 0 0 1 6 8 10 10
11. 1 0 1 0 7 9 8 11
12. 1 0 1 1 19 6 1 2
13. 1 1 0 0 21 18 7 19
14. 1 1 0 1 11 15 9 5
15. 1 1 1 0 23 20 10 8
16. 1 1 1 1 86 42 2 4
Stack variables cwm, cwf, cbm and cbf into a single frequency variable wt2 and create dummies w for white and m for male
gen i=_n
reshape long cw cb,i(i) j(male) string
replace i=_n
reshape long c, i(i) j(white) string
drop i
encode white, gen(w)
encode male, gen(m)
replace w=w-1
replace m=m-1
rename c wt2
list in 1/10, clean nolab
white male y1 y2 y3 y4 wt2 w m
1. b f 0 0 0 0 29 0 0
2. w f 0 0 0 0 20 1 0
3. b m 0 0 0 0 27 0 1
4. w m 0 0 0 0 23 1 1
5. b f 0 0 0 1 8 0 0
6. w f 0 0 0 1 8 1 0
7. b m 0 0 0 1 5 0 1
8. w m 0 0 0 1 5 1 1
9. b f 0 0 1 0 7 0 0
10. w f 0 0 1 0 14 1 0
Calculate tot, the sizes of the four groups defined by w and m
egen tot = sum(wt2), by(w m)
Stack responses y1 to y4 into a single vector and create variable item
gen patt=_n
reshape long y, i(patt) j(item)
list in 1/8, clean nolab
patt item white male y wt2 w m
1. 1 1 b f 0 29 0 0
2. 1 2 b f 0 29 0 0
3. 1 3 b f 0 29 0 0
4. 1 4 b f 0 29 0 0
5. 2 1 w f 0 20 1 0
6. 2 2 w f 0 20 1 0
7. 2 3 w f 0 20 1 0
8. 2 4 w f 0 20 1 0
Create dummy variables d1 to d4 for items 1 to 4
qui tab item, gen(d)
Estimate the one-parameter logistic IRT model (Table 9.5)
gllamm y d1 d2 d3 d4, i(patt) l(logit) f(binom) weight(wt) nocons adapt
number of level 1 units = 3104
number of level 2 units = 776
Condition Number = 1.6838733
gllamm model
log likelihood = -2004.9379
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d1 | .5775969 .0969974 5.95 0.000 .3874854 .7677083
d2 | .2382793 .0950415 2.51 0.012 .0520014 .4245572
d3 | -.2247582 .0949752 -2.37 0.018 -.4109062 -.0386102
d4 | -.5938583 .0971079 -6.12 0.000 -.7841863 -.4035303
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and covariances of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (patt)
var(1): 1.6285398 (.20840709)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
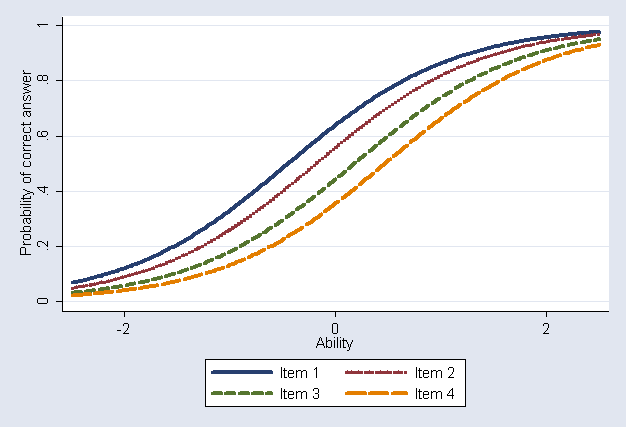
Plot the item characteristic curves (Figure 9.5)
matrix list e(b)
e(b)[1,5]
y: y: y: y: patt1:
d1 d2 d3 d4 _cons
y1 .57759686 .23827933 -.22475821 -.59385829 1.2761425
twoway (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d1 -x*[patt1]_cons)), range(-2.5 2.5)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d2 -x*[patt1]_cons)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(dot)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d3 -x*[patt1]_cons)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(dash)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d4 -x*[patt1]_cons)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(longdash)), /*
*/ legend( label(1 "Item 1") label(2 "Item 2") label(3 "Item 3") label(4 "Item 4") ) /*
*/ xtitle(Ability) ytitle(Probability of correct answer)
eq load: d1-d4
gllamm y d1-d4, i(patt) eqs(load) l(logit) f(binom) weight(wt) nocons adapt nip(12)
number of level 1 units = 3104
number of level 2 units = 776
Condition Number = 5.4532607
gllamm model
log likelihood = -2002.7391
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d1 | .6453275 .1206319 5.35 0.000 .4088932 .8817617
d2 | .2194106 .0890237 2.46 0.014 .0449274 .3938939
d3 | -.2156426 .0908816 -2.37 0.018 -.3937672 -.037518
d4 | -.6251801 .109345 -5.72 0.000 -.8394923 -.4108678
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and covariances of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (patt)
var(1): 2.6007398 (.87041805)
loadings for random effect 1
d1: 1 (fixed)
d2: .64650121 (.15490565)
d3: .69484866 (.16864938)
d4: .89729467 (.21828051)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The variance and factor loading estimates differ a little from those in Table 9.5.
Plot item characteristic curves (Figure 9.5)
matrix list e(b)
e(b)[1,8]
y: y: y: y: pat1_1l: pat1_1l: pat1_1l:
d1 d2 d3 d4 d2 d3 d4
y1 .64532747 .21941063 -.21564261 -.62518007 .64650121 .69484866 .89729467
pat1_1:
d1
y1 1.6126809
twoway (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d1 -x*[pat1_1]d1)), range(-2.5 2.5)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d2 -x*[pat1_1]d1*[pat1_1l]d2)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(dot)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d3 -x*[pat1_1]d1*[pat1_1l]d3)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(dash)) /*
*/ (function y=1/(1+exp(-[y]d4 -x*[pat1_1]d1*[pat1_1l]d4)), range(-2.5 2.5) clpatt(longdash)), /*
*/ legend( label(1 "Item 1") label(2 "Item 2") label(3 "Item 3") label(4 "Item 4") ) /*
*/ xtitle(Ability) ytitle(Probability of correct answer)
Estimate two-parameter IRT model with non-zero mean ability, setting the item difficulty of item 1 to zero (Table 9.6)
gen cons=1
eq load: d1-d4
eq f1: cons
gllamm y d2-d4, i(patt) eqs(load) l(logit) f(binom) weight(wt) /*
*/ geqs(f1) nocons adapt nip(12)
number of level 1 units = 3104
number of level 2 units = 776
Condition Number = 6.9163564
gllamm model
log likelihood = -2002.7391
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d2 | -.197791 .1174163 -1.68 0.092 -.4279228 .0323408
d3 | -.6640437 .1352743 -4.91 0.000 -.9291764 -.398911
d4 | -1.204219 .1846912 -6.52 0.000 -1.566207 -.8422309
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and covariances of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (patt)
var(1): 2.6008217 (.87044376)
loadings for random effect 1
d1: 1 (fixed)
d2: .64648882 (.15490305)
d3: .69483564 (.1686465)
d4: .89727244 (.21827359)
Regressions of latent variables on covariates
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
random effect 1 has 1 covariates:
cons: .64533407 (.12063317)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The estimates differ a little from those in Table 9.6.
Empirical Bayes predictions: EAP ability scores
gllapred IRT, fac (means and standard deviations will be stored in IRTm1 IRTs1)
Estimate a MIMIC model where ability depends on sex (dummy f), race (dummy b) and their interaction (Table 9.6)
gen f=1-m
gen b=1-w
gen b_f = b*f
eq f1: cons f b b_f
matrix a=e(b)
gllamm y d2-d4, i(patt) eqs(load) l(logit) f(binom) weight(wt) /*
*/ geqs(f1) from(a) nocons adapt nip(12)
number of level 1 units = 3104
number of level 2 units = 776
Condition Number = 10.407055
gllamm model
log likelihood = -1956.2333
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
y | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
d2 | -.2114786 .1159544 -1.82 0.068 -.4387451 .015788
d3 | -.7145968 .1379683 -5.18 0.000 -.9850096 -.4441839
d4 | -1.159195 .1601593 -7.24 0.000 -1.473101 -.8452882
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and covariances of random effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
***level 2 (patt)
var(1): 1.9689171 (.60516363)
loadings for random effect 1
d1: 1 (fixed)
d2: .67658546 (.14380046)
d3: .77264707 (.16674369)
d4: .86240868 (.17342379)
Regressions of latent variables on covariates
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
random effect 1 has 4 covariates:
cons: 1.4345373 (.21553973)
f: -.6200911 (.20526977)
b: -1.6843558 (.31129702)
b_f: .67057381 (.32116754)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The estimates differ a little from those in Table 9.6.
Empirical Bayes predictions: EAP ability scores
gllapred MIMIC, fac (means and standard deviations will be stored in MIMICm1 MIMICs1)
Look at ability scores for each response and covariate pattern (Table 9.7)
drop d1-d4
reshape wide y, i(patt) j(item)
sort y1-y4 b f
list y1-y4 b f IRTm1 MIMICm1, nolab clean
y1 y2 y3 y4 b f IRTm1 MIMICm1
1. 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1.2242641 -.55473277
2. 0 0 0 0 0 1 -1.2242641 -.87608943
3. 0 0 0 0 1 0 -1.2242641 -1.4707461
4. 0 0 0 0 1 1 -1.2242641 -1.4410752
5. 0 0 0 1 0 0 -.14876 .26704248
6. 0 0 0 1 0 1 -.14876 -.02615521
7. 0 0 0 1 1 0 -.14876 -.54782301
8. 0 0 0 1 1 1 -.14876 -.52233467
9. 0 0 1 0 0 0 -.37675812 .18398721
10. 0 0 1 0 0 1 -.37675812 -.11085131
11. 0 0 1 0 1 0 -.37675812 -.63777142
12. 0 0 1 0 1 1 -.37675812 -.6119613
13. 0 0 1 1 0 0 .60364936 .97836482
14. 0 0 1 1 0 1 .60364936 .68778691
15. 0 0 1 1 1 0 .60364936 .19041653
16. 0 0 1 1 1 1 .60364936 .21416676
17. 0 1 0 0 0 0 -.43218061 .09469579
18. 0 1 0 0 0 1 -.43218061 -.20221901
19. 0 1 0 0 1 0 -.43218061 -.73534825
20. 0 1 0 0 1 1 -.43218061 -.70916483
21. 0 1 0 1 0 0 .55196233 .8893892
22. 0 1 0 1 0 1 .55196233 .59958378
23. 0 1 0 1 1 0 .55196233 .10115863
24. 0 1 0 1 1 1 .55196233 .12502831
25. 0 1 1 0 0 0 .33515561 .80656055
26. 0 1 1 0 0 1 .33515561 .51719789
27. 0 1 1 0 1 0 .33515561 .01729505
28. 0 1 1 0 1 1 .33515561 .0413004
29. 0 1 1 1 0 0 1.3035676 1.6228636
30. 0 1 1 1 0 1 1.3035676 1.3180372
31. 0 1 1 1 1 0 1.3035676 .81295145
32. 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.3035676 .83659008
33. 1 0 0 0 0 0 -.0351866 .3938274
34. 1 0 0 0 0 1 -.0351866 .10259226
35. 1 0 0 0 1 0 -.0351866 -.41203827
36. 1 0 0 0 1 1 -.0351866 -.38699316
37. 1 0 0 1 0 0 .93089004 1.1908602
38. 1 0 0 1 0 1 .93089004 .89722329
39. 1 0 0 1 1 0 .93089004 .40020559
40. 1 0 0 1 1 1 .93089004 .42377722
41. 1 0 1 0 0 0 .71352262 1.1065918
42. 1 0 1 0 0 1 .71352262 .81436966
43. 1 0 1 0 1 0 .71352262 .31757081
44. 1 0 1 0 1 1 .71352262 .34119563
45. 1 0 1 1 0 0 1.7045824 1.9484446
46. 1 0 1 1 0 1 1.7045824 1.6312163
47. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.7045824 1.113084
48. 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.7045824 1.1371117
49. 1 1 0 0 0 0 .66179647 1.0169609
50. 1 1 0 0 0 1 .66179647 .72595346
51. 1 1 0 0 1 0 .66179647 .22887171
52. 1 1 0 0 1 1 .66179647 .25257845
53. 1 1 0 1 0 0 1.6485285 1.8501881
54. 1 1 0 1 0 1 1.6485285 1.5370316
55. 1 1 0 1 1 0 1.6485285 1.0234149
56. 1 1 0 1 1 1 1.6485285 1.0472972
57. 1 1 1 0 0 0 1.4181578 1.7596042
58. 1 1 1 0 0 1 1.4181578 1.4499547
59. 1 1 1 0 1 0 1.4181578 .9400666
60. 1 1 1 0 1 1 1.4181578 .96383584
61. 1 1 1 1 0 0 2.506591 2.6876937
62. 1 1 1 1 0 1 2.506591 2.3322937
63. 1 1 1 1 1 0 2.506591 1.7665629
64. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2.506591 1.7923462
The scores differ a little from those in Table 9.7.
Mislevy, R. J. (1985). Estimation of latent group effects. Journal of the American Statistical Association 80, 993-997.
Skrondal, A. and Rabe-Hesketh, S. (2004). Generalized
Latent Variable Modeling: Multilevel, Longitudinal and Structural
Equation Models. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press.
Outline
Datasets and do-files